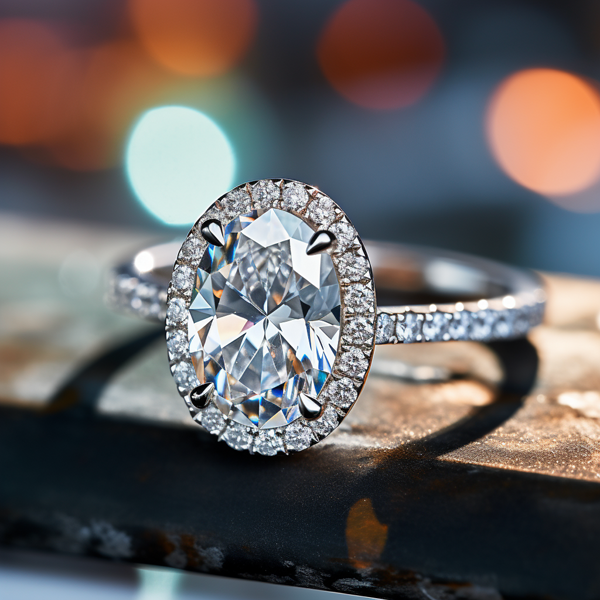
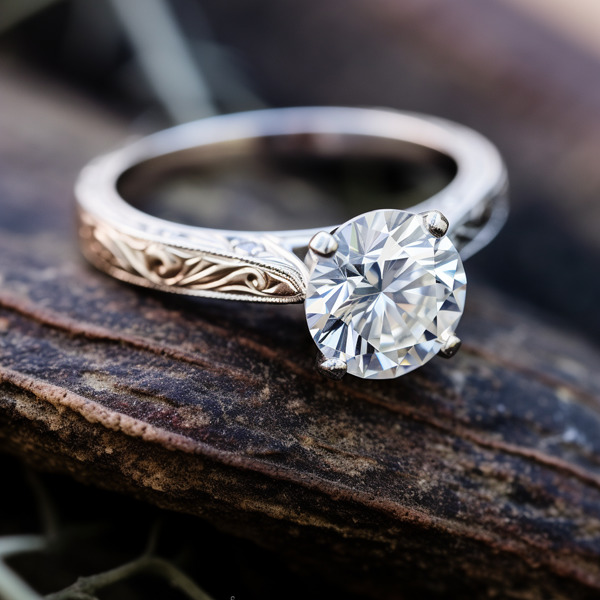
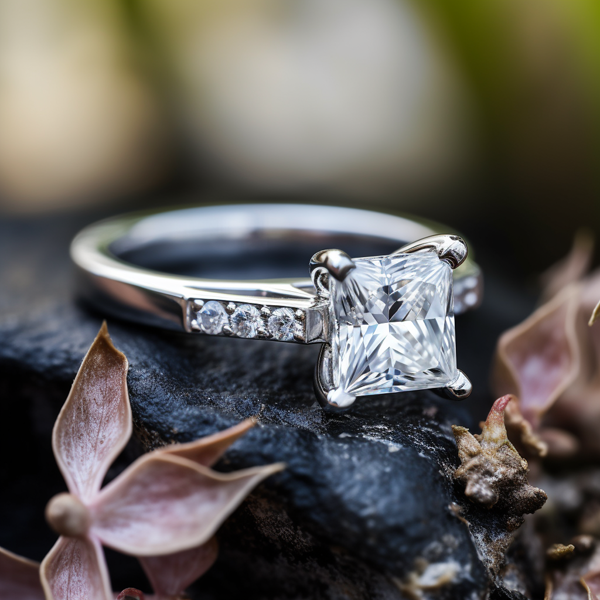
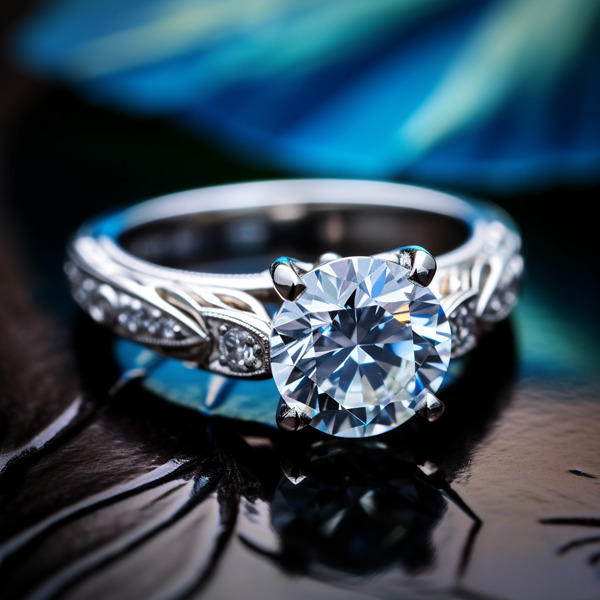
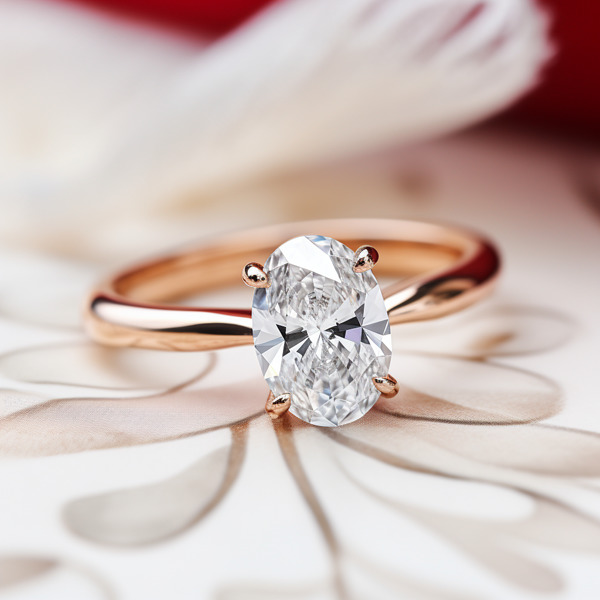
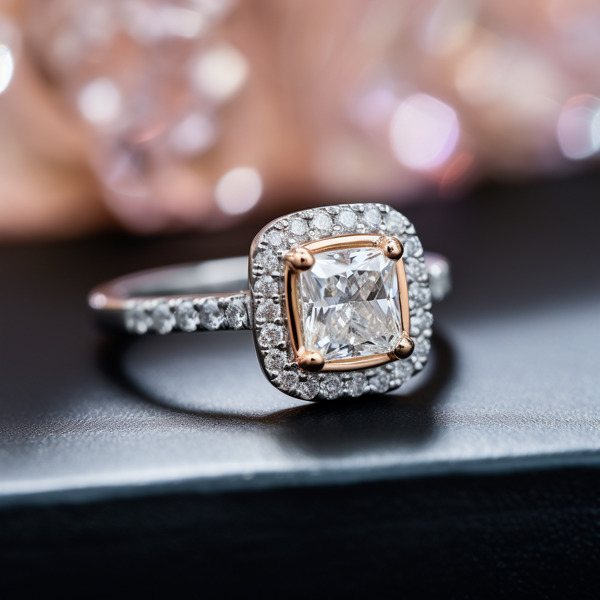
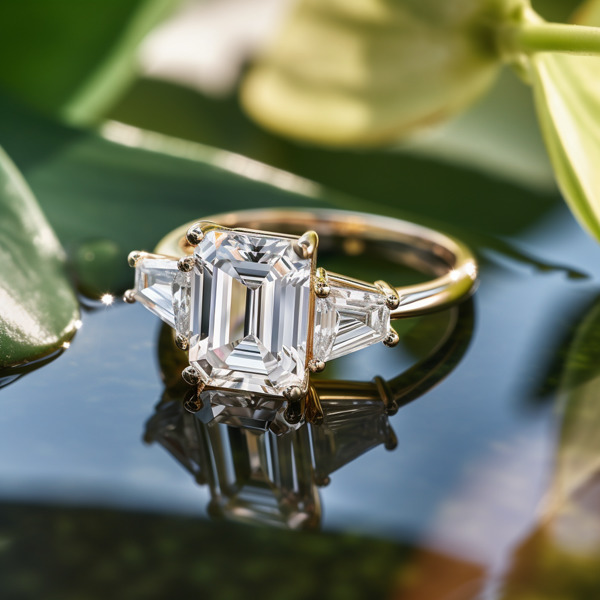
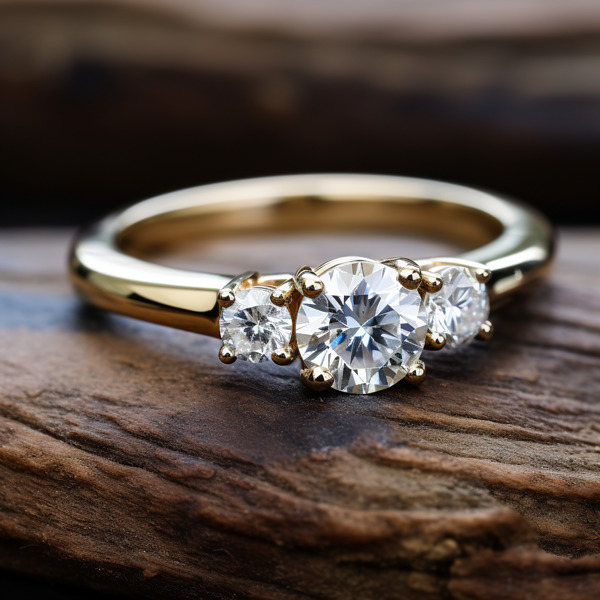
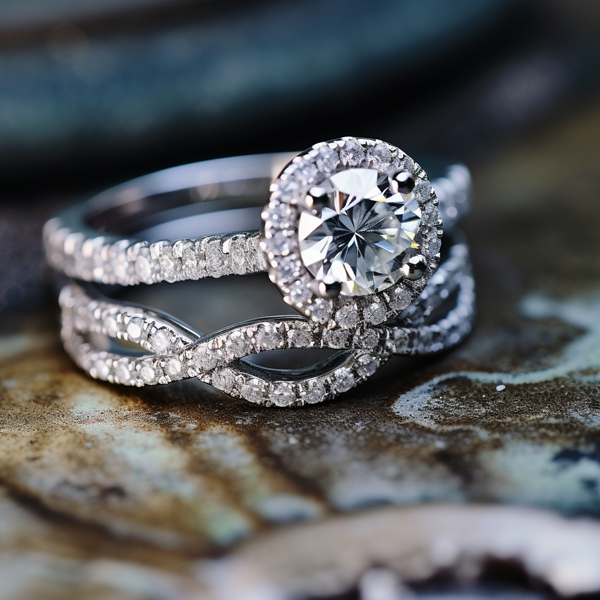
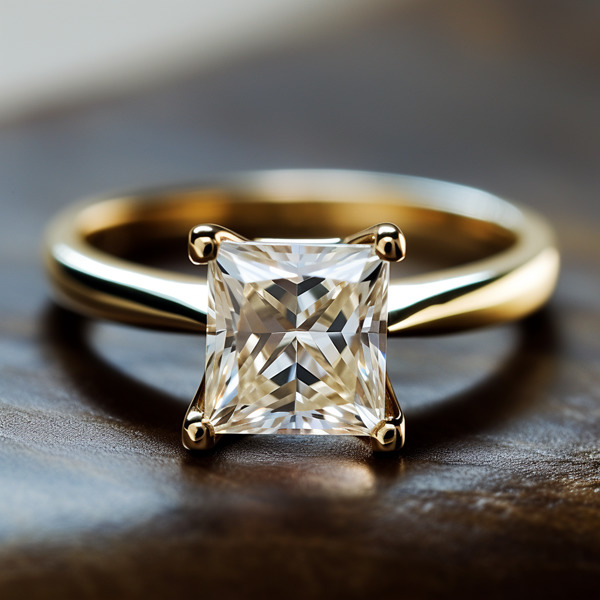
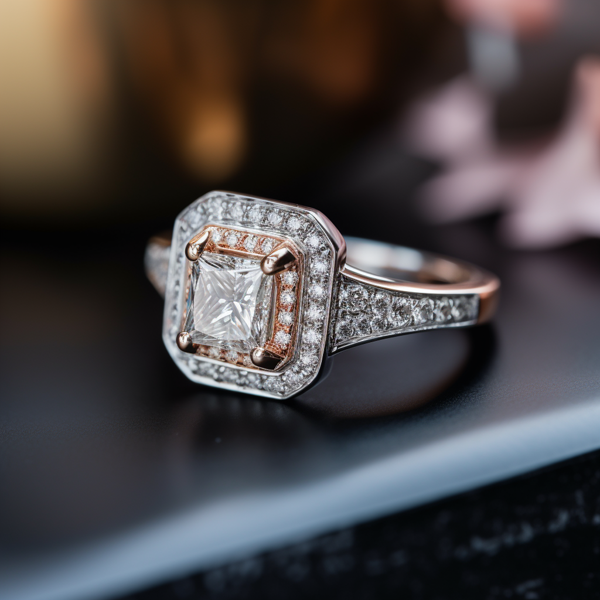
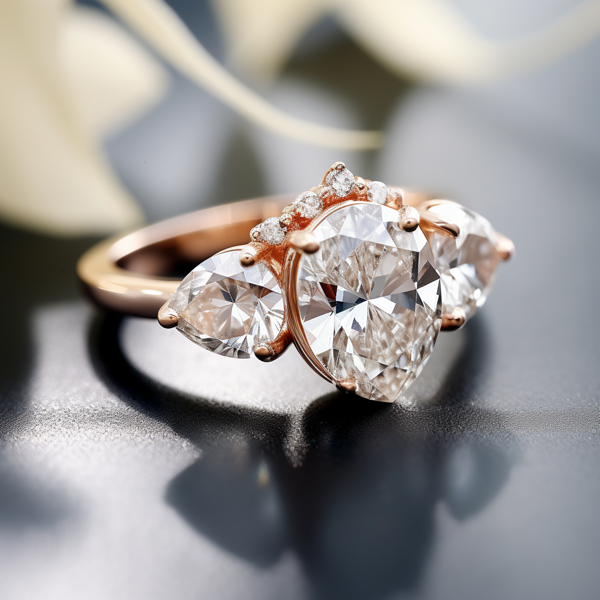
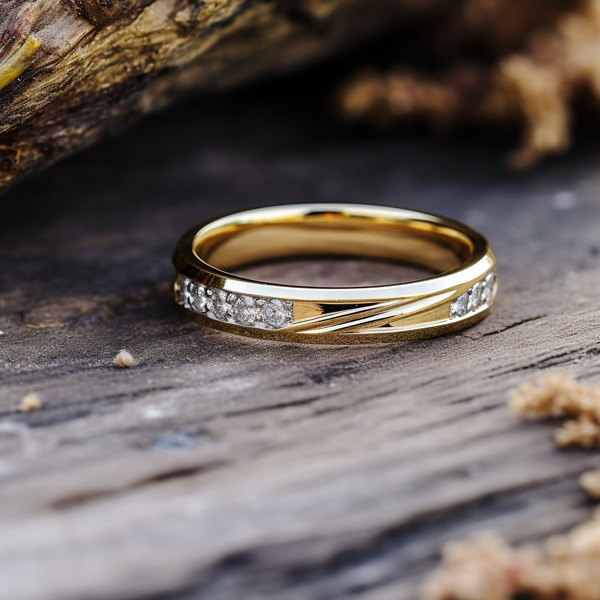
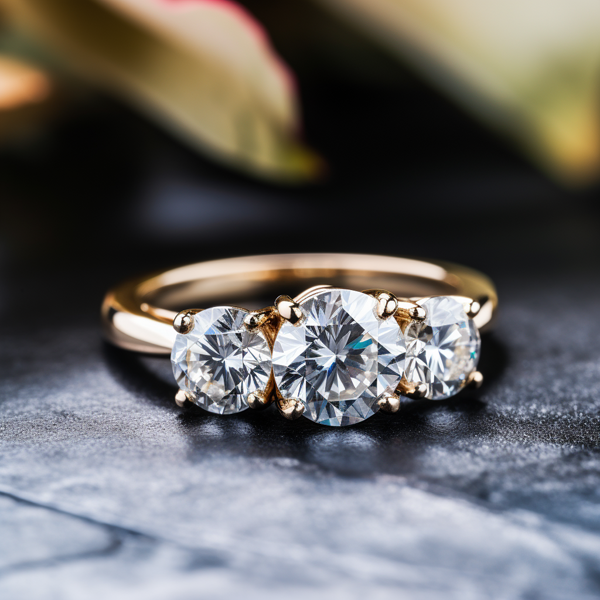
Key Takeaways:
- Lab-grown diamonds offer the same characteristics as natural diamonds but at a lower price point. They are chemically and optically identical to mined diamonds.
- Buying lab-grown diamond rings online can offer a wide range of options and a convenient shopping experience. Reputable online retailers like James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, and Kay Jewelers provide reliable sources for purchasing lab-grown diamonds.
- When buying lab-grown diamond rings online, it is important to consider the 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Authenticity and certification should also be verified, and visual inspection, customer reviews, and feedback can aid in decision-making.
- Choosing the perfect lab-grown diamond ring involves considering factors such as shape, cut quality, setting style, band design, and the appeal of colorless and eye-clean diamonds. Certifications, the purchase process, payment options, returns, exchanges, and warranties should also be taken into account.
- The popularity of lab-grown diamond rings is increasing due to their affordability, ethical implications, and environmental sustainability. The future of lab-grown diamonds looks promising, as technology continues to advance and more consumers embrace this alternative to mined diamonds.
Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Gary Torres
Looking to buy a lab-grown diamond ring online? In this introduction, we will explore the world of lab-grown diamonds, their unique characteristics, and why choosing a lab-grown diamond ring can be a beneficial option. Get ready to uncover the fascinating facts, figures, and events surrounding lab-grown diamonds as we dive into what sets them apart and why they have become a popular choice for modern-day buyers.
Definition and Characteristics of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are not formed naturally, but rather “created in a laboratory.” They have the same chemical and physical properties as natural diamonds, such as hardness, brilliance, and fire. This makes them indistinguishable to the naked eye. These gems are a sustainable and ethical alternative to mined diamonds, as they don’t contribute to environmental damage or human rights issues.
These man-made diamonds are produced in a lab, using techniques that mimic natural diamond formation. They possess the same qualities as mined diamonds – including their durability and brilliance. Plus, the same 4Cs (cut, color, clarity, carat weight) are used to grade them.
When searching for lab-grown diamond rings online, look for reputable retailers like James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, and Kay Jewelers. Be sure to understand the importance of certification when buying. Gemological laboratories provide certificates to verify authenticity and quality. Visual inspection and comparison tools can help assess factors like cut quality, color grade, clarity grade, and carat weight.
It’s also wise to examine reviews and customer feedback. This can guide the decision and provide confidence in the quality and authenticity of the diamonds.
Benefits of Buying Lab-Grown Diamond Rings
Lab-grown diamond rings boast a variety of advantages! These diamonds are crafted in laboratories, using tech that mimics the natural diamond formation. They contain the same physical and chemical components as natural diamonds, making them indistinguishable to the eye. Plus, they cost less, so you can get bigger or higher quality stones within your budget. And, they are free from unethical mining, which appeals to environmentally conscious customers.
Plus, there’s more:
- Superior Value: Lab-grown diamond rings offer superior value compared to natural diamonds.
- Larger Stones: Buyers can now afford larger stones than they would with natural diamonds.
- Higher Quality: The lower cost of lab-grown diamonds allows buyers to go for higher quality in terms of color, clarity, and cut.
- Ethical Sourcing: Lab-grown diamonds eliminate the ethical issues that come with traditional diamond mining, such as human rights violations and conflict.
- Sustainability: These diamonds have a smaller environmental effect since they don’t require mining or other harmful activities.
Furthermore, lab-grown diamond rings come with certifications that guarantee their authenticity and quality. Reviews and consumer feedback are also available online, to give customers confidence in their purchase. Check out established online retailers like James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, or Kay Jewelers!
Ready to find the perfect lab-grown diamond online? Hold on tight, ’cause we’re about to take you on a carat ride!
Factors to Consider When Buying Lab-Grown Diamond Rings Online

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Gabriel Smith
Considering authenticity, certification, visual inspection, and customer reviews are key factors when buying lab-grown diamond rings online, this section will provide valuable insights into reputable online retailers for lab-grown diamonds, the importance of understanding the 4Cs, and how to ensure the authenticity and quality of your purchase through visual inspection and customer feedback.
Reputable Online Retailers for Lab-Grown Diamonds
Online sellers are vital in the lab-grown diamond market. They give customers many choices and convenience. Check out these reliable online sellers for lab-grown diamonds:
- James Allen: With a huge selection and high-tech features, James Allen has certified lab-grown diamond rings.
- Blue Nile: As a big online diamond seller, Blue Nile offers various lab-grown diamond rings for different budgets. They provide all the facts about each diamond’s 4Cs.
- Brilliant Earth: Emphasizing ethical sourcing and sustainability, Brilliant Earth has lab-grown diamond rings made with care. They provide customers with education about lab-grown diamonds and custom options.
- Rare Carat: Rare Carat is an online platform with prices and specs from different sellers. It’s a transparent market for buyers.
- Kay Jewelers: With many jewelry choices, Kay Jewelers also sells lab-grown diamond rings. They have a great name for customer service and satisfaction.
These online sellers are reliable because of their reputations, quality items, certification processes, and positive customer feedback. When buying a lab-grown diamond ring online, these options should be considered.
Besides these online sellers, other things to consider when buying a lab-grown diamond ring online are the 4Cs – cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Authenticity should also be checked with certification. Visual examination and comparison are important too. Look at images and videos from various angles. Read reviews and customer feedback for the seller’s products and services.
James Allen
Buy a lab-grown diamond ring online? James Allen is the place to go! With an extensive selection and detailed product info, finding the perfect diamond ring is easy. Their user-friendly interface makes navigation and comparison of different options a breeze.
James Allen’s innovative Ring Resizing Service is unique. Customers can resize their purchased rings within 60 days of delivery for free, once per order. This adds value and ensures satisfaction.
Need a lab-grown diamond? Look no further – Blue Nile has got you covered.
Blue Nile
Blue Nile – a reputable retailer for lab-grown diamonds – is ideal for customers seeking diamond rings. They offer a wide range of shapes & cuts. Plus, setting styles & band designs to customize. Their focus? Colorless & eye-clean diamonds of high quality. Complete with authenticity & certification. Also, reviews & customer feedback for reliability & satisfaction. The perfect spot to purchase lab-grown diamond rings online!
Brilliant Earth
When scoping out lab-grown diamond rings online, Brilliant Earth is an ace option to consider. They’re a dependable online retailer, known for their ethical practices and sustainable sourcing. The 4Cs of lab-grown diamonds are important for determining quality and value. Cut, color, clarity, and carat weight must be graded accurately, and Brilliant Earth makes sure of this.
Authenticity and certification are a must when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. Brilliant Earth has proof for each diamond they sell, including certifications from well-known gemological laboratories, like the GIA. This guarantees that the diamonds meet industry standards and have been tested and evaluated properly.
Examining and comparing helps when deciding to buy. Brilliant Earth offers high-quality images and videos of their lab-grown diamond rings on their website. Plus, reviews and customer feedback are helpful when it comes to the overall shopping experience with Brilliant Earth.
To sum up, Brilliant Earth is a great place for buying lab-grown diamond rings. Their selection is top-notch, they provide certification and visual inspection, and have great customer feedback. Look no further for lab-grown diamond rings than Brilliant Earth.
Rare Carat
Rare Carat is the go-to spot for those who crave lab-grown diamond rings! Customers can filter searches based on the 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Each diamond’s authenticity and certification are also displayed, giving customers peace of mind. Plus, customer reviews help ensure informed decisions. When it comes to lab-grown diamonds, Rare Carat provides an easy and reliable online shopping experience!
One customer shared her successful story: she was hesitant at first but found her perfect ring after comparing different diamonds. And the quality and appearance exceeded her expectations. She recommends Rare Carat to anyone looking for lab-grown diamonds – sparkle responsibly!
Kay Jewelers
When thinking of buying lab-grown diamond rings from Kay Jewelers, there are 4 things to consider: Cut, Color, Clarity and Carat Weight.
The Cut decides how well the diamond reflects light, giving it its sparkle. Kay Jewelers has a range of cut options like round, princess, and cushion.
Color is another factor. Lab-grown diamonds come in different colors, but many pick colorless or near-colorless for engagement rings. Kay Jewelers has white and tinted diamonds for customers to choose from.
Clarity is important too. It means the presence or absence of flaws or inclusions within the diamond. Kay Jewelers makes sure their diamonds are eye-clean with no visible flaws.
Carat weight is also a factor. It determines the size of the diamond, with higher carat weights being bigger and more expensive. Kay Jewelers has a selection of carat weights to suit everyone’s needs.
Furthermore, it’s important to check the authenticity and certification of the lab-grown diamond ring from Kay Jewelers. They provide certificates issued by independent gemological laboratories, guaranteeing authenticity and quality.
Kay Jewelers has been widely praised for its customer service. They have received many positive reviews from customers who bought lab-grown diamond rings. This shows why they are a top online retailer for lab-grown diamonds.
So, when it comes to lab-grown diamonds, remember the 4Cs! Cut, Color, Clarity and Carat Weight – they make or break your dreams.
The 4Cs of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are made in a lab, instead of being mined from the earth. They have the same properties as natural diamonds, making them hard to distinguish. One of the benefits of such diamonds is they are usually cheaper than their natural counterparts.
The 4Cs of lab-grown diamonds refer to cut, color, clarity and carat weight. These factors decide the diamond’s worth. Cut shapes like round, princess or emeralds can maximize the diamond’s sparkle.
- When it comes to color, lab-grown diamonds come in many hues, from colorless to fancy colors like yellow or pink.
- Clarity refers to flaws within a diamond. Lab-grown diamonds usually have fewer inclusions due to their controlled growth environment.
- Carat weight determines the diamond’s size and weight. Lab-grown diamonds come in various carat weights, allowing customers to pick based on their budget.
The 4Cs of lab-grown diamonds are important, but their importance may vary depending on personal preferences. Finding the right lab-grown diamond is like finding a needle in a diamond-studded haystack.
Cut
- Proportions: Determine how light reflects in a stone. Ideal ones give maximum light dispersion. Result? A brilliant sparkle!
- Facets: Number and arrangement affect appearance. Each one reflects light differently, enhancing brilliance.
- Polish: Determines surface quality and smoothness. A well-polished lab-grown diamond has no visible flaws.
- Symmetry: Alignment and balance of facets. Precisely symmetrical lab-grown one looks great from all angles.
- Brilliance: How facets interact with light. A well-cut lab-grown one reflects and refracts light, creating fire and sparkle.
Lab-grown diamonds come in round, princess, emerald, and cushion cuts. Each one has unique traits, so pick the style you like.
When buying a lab-grown diamond ring, check its quality. Round-cut diamonds are known for their brilliance. Princess-cut ones offer a modern look.
To get the perfect cut, explore online resources. Check high-resolution images and videos. Also, read customer reviews and feedback.
By considering technical aspects and your preferences, you can select a lab-grown diamond ring with a cut that enhances its beauty. Find the right combination of cut and style for a breathtaking lab-grown diamond ring.
Color
It’s vital to consider color grade when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. The table below presents the different color grades available:
| Color Grade |
Description |
| D |
Colorless |
| E-F |
Almost Colorless |
| G-H |
Near-Colorless |
| I-J |
Faint Yellow or Brown Tint |
| K-L |
Very Light Yellow |
| M-Z |
Light Yellow or Brown |
Higher grades, like D and E-F, have a pure white appearance which is sought after for engagement rings. Lower grades, like M-Z, have a noticeable yellow or brown tint. Personal preference and metal for the setting can influence the color too. So, choose the color grade that suits your taste and style.
Clarity
It’s important to understand the different clarity grades when purchasing a lab-grown diamond. Higher grades (Flawless or Internally Flawless) are rarer, and usually cost more. Although, diamonds with slightly lower grades (Very Slightly Included or Slightly Included) may look flawless to the eye.
Inclusions don’t always indicate low quality. They can be unique and add character to a diamond. However, when selecting a lab-grown diamond, it’s best to balance between uniqueness and visual appeal.
Carat Weight
Carat weight is an important factor to consider when selecting a lab-grown diamond ring. However, it is not the only thing to think about. Cut, color, and clarity are also essential criteria that determine the overall quality and value of the diamond. For the best outcome, it is best to find a balance between carat weight and these other characteristics.
I searched online for the ideal lab-grown diamond ring. Many retailers had visuals and detailed info on carat weight, making it easier to compare different options. Customer reviews and feedback were also helpful when making a decision. In the end, I was able to find a perfect lab-grown diamond that fit my budget and style!
Authenticity and Certification
For lab-grown diamonds, it’s essential to know the retailer’s info. Sites like James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, and Kay Jewelers make it clear where the diamonds come from, how they’re made, and their grading criteria. This helps customers make an informed decision on the diamond’s authenticity.
Certification is another factor to consider. GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and IGI (International Gemological Institute) are two gemological labs that provide certifications for lab-grown diamonds. These certify quality, authenticity, and the 4Cs – cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Plus, they show if a diamond is natural or lab-grown.
Remember, not all lab-grown diamonds have certifications. Some companies provide their own grading reports. In these cases, customers should check customer reviews and expert opinions to make sure they’re reliable.
Pro Tip: Get lab-grown diamonds with third-party certifications. This ensures authenticity and quality.
Visual Inspection and Comparison
Reputable online retailers provide detailed product descriptions, high-resolution images, and even videos of the lab-grown diamonds they offer. This helps customers to see the cut, color, clarity, and carat weight in detail. They can check the diamond’s brilliance, sparkle, and beauty before deciding to buy.
In addition, some retailers offer interactive tools for customers to compare diamonds. They can check multiple diamonds simultaneously and analyze their 4Cs.
Customer reviews are also important for visual inspection and comparison. People can read other buyers’ thoughts on similar lab-grown diamond rings. This helps them learn if there is any difference between what was advertised and what they got.
Overall, visual inspection and comparison are essential steps when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. This allows customers to examine different options while ensuring quality representations are transparent.
Reviews and Customer Feedback
Reviews and customer feedback are a must when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. They give valuable insights into quality, service and the experience. These views show the satisfaction of other buyers, aiding potential customers to judge authenticity and dependability.
Furthermore, reviews help customers rate the quality of diamonds from different online stores. Cut, color, clarity, and carat weight are often talked about, giving beneficial info for making wise buys.
Positive reviews and customer feedback create trust and act as social proof for online stores. By taking these reviews into account, potential purchasers can feel more secure about their choice.
It’s essential to check reviews and customer feedback on multiple platforms to understand the overall reputation of an online retailer. This makes it easy to compare options and make knowledgeable purchase decisions.
Making a Purchase

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Zachary White
When it comes to making a purchase for a lab-grown diamond ring online, there are a few key aspects to consider. In this section, we will explore how to choose the perfect lab-grown diamond ring, the importance of certification, the purchase process and payment options, as well as the details regarding returns, exchanges, and warranties. So, let’s dive into the essential factors to ensure a smooth and satisfactory experience when buying a lab-grown diamond ring online.
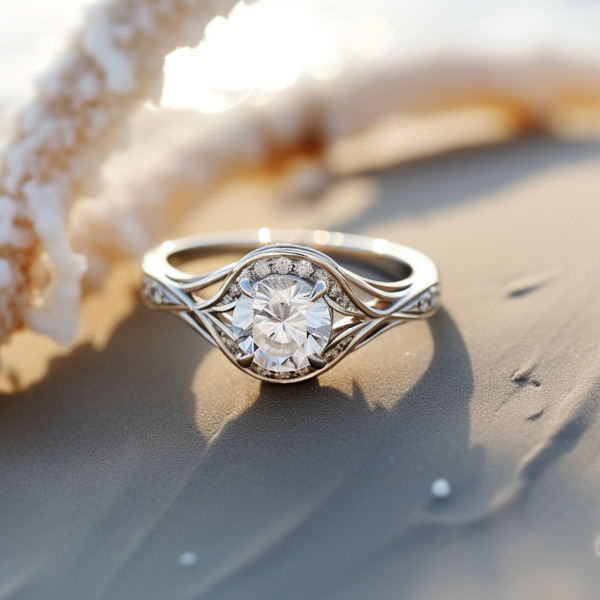
Choosing the Perfect Lab-Grown Diamond Ring
Choose the perfect lab-grown diamond ring with care. Know the factors that make a ring special. These include shape, cut quality, setting style, band design, colorlessness, and certification.
Shape and cut: Pick a style that suits you – round or princess. Make sure it’s expertly crafted for sparkle.
Setting and band: Choose a style to show off the diamond. Platinum or gold can personalize it.
Colorless and eye-clean: Colorless diamonds have great clarity. Eye-clean diamonds have no visible flaws.
Certification: Get certification from GIA or IGI to verify the diamond’s quality.
Know these key factors and make informed decisions. Get a diamond ring that’s cut above the rest.
Shape and Cut Quality
Shape and cut quality are essential when buying lab-grown diamond rings. Different shapes, such as round, princess, emerald, and pear, have unique characteristics. The cut quality affects the diamond’s brilliance, with a well-cut diamond reflecting light for maximum sparkle and fire.
Proportions also matter – ideal ones ensure proper reflection and refraction of light, creating exceptional sparkle. Different cutting styles, such as brilliant cut, step cut, or mixed cut, can enhance the appearance of a lab-grown diamond.
Cut grades from gemological labs indicate superior cutting quality. When buying a lab-grown diamond ring online, it is important to focus on shape and cut quality. The right combination can elevate the beauty and show your personal style.
Research different shapes and consider higher cut grades. Use images and videos to inspect the shape and cut of each lab-grown diamond ring. Consult with gemologists and read customer reviews to gauge the reputation and reliability of retailers.
By focusing on shape and cut quality, you can get a visually appealing lab-grown diamond ring with exceptional brilliance. Consider these factors to make an informed decision that aligns with your taste.
Setting Style and Band Design
If you’re selecting a lab-grown diamond ring, here’s a 6-step guide to consider:
- Pick your preferred setting style. Options include prong, bezel, halo, pave, and channel. Think about your personal taste and how you’d like the diamond to be seen.
- Choose a metal for the band. Common options are white gold, yellow gold, rose gold, platinum, and silver. Consider your skin tone and what you like.
- Decide if you want extra gemstones or accents. Adding some sparkle or color to your ring can be nice. Options include side stones and accent diamonds along the band.
- Select a band width that suits your hand. Narrower bands suit smaller hands and wider bands make a bolder statement.
- Think about lifestyle and comfort. If you lead an active lifestyle, opt for a secure setting that won’t snag or get in the way.
- Personalize with engraving or custom designs. Many retailers offer the option to add a special message or custom details.
When selecting a diamond, remember: it’s all about finding the right balance between clarity and invisibility.
Colorless Diamonds and Eye-Clean Diamonds
Colorless diamonds and eye-clean diamonds are two key factors to consider when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. Colorless diamonds are popular for their perfect, pure look. They are graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). These diamonds let maximum light through, making them sparkle.
Eye-clean diamonds have no visible inclusions or blemishes when seen with the eye. Inclusions refer to internal flaws, while blemishes are external. To be eye-clean, the diamond should have a high clarity grade, from Flawless (no visible inclusions or blemishes under 10x magnification) to VS1/VS2 (hard to notice without magnification).
When buying lab-grown diamond rings online, look at product descriptions carefully. These should provide info on the color grade and clarity grade. Reviews also give valuable insights into how well these qualities are portrayed in the ring.
By choosing a colorless diamond with good cut quality and an eye-clean stone with high clarity, you can be sure of the beauty and value of the ring. Certification is essential – it’s like a cat claiming to be a unicorn without it!
The Importance of Certification
When it comes to buying lab-grown diamond rings, certification is hugely important. Consumers must make sure they are getting genuine diamonds made in a lab, not from the earth. Certification gives assurance about the diamond’s source, quality, and ethical sourcing.
Independent grading labs certify lab-grown diamonds to check their quality and characteristics. These certifications provide info on the diamond’s 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. The cut is about how well the diamond is shaped and faceted. Color grades go from colorless to yellow or brown. Clarity shows if there are any internal or external flaws. Carat weight is the size.
GIA and IGI are reputable grading labs providing certifications which add credibility and transparency to the purchase. They give accurate assessments of the diamond’s attributes, so customers know what they’re getting.
Certification is great for verifying the quality and value of a lab-grown diamond ring. It’s also proof of authenticity if you resell the ring or need insurance.
Now, let’s look at how to buy a lab-grown diamond ring. We’ll also discuss payment options, as financial planning is essential when making this purchase.
The Purchase Process and Payment Options
Lab-grown diamonds are an environmentally friendly and ethical alternative to traditional mined diamonds. Shopping for a lab-grown diamond ring online requires a careful purchase process and consideration of various payment options. Reputable online retailers, such as James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, and Kay Jewelers, offer convenient platforms for purchasing lab-grown diamond rings. Factors like the 4Cs (cut, color, clarity, and carat weight) should be taken into account. Authentication and certification are also necessary to ensure the quality of the lab-grown diamond. Visual inspection, comparison, reviews, and customer feedback can help make an informed decision.
Shape, cut quality, setting style, band design, colorless diamonds, and eye-clean diamonds should all be considered when selecting the perfect lab-grown diamond ring. Certification is essential to guarantee that the lab-grown diamond meets industry standards. The purchase process usually involves browsing through options online, selecting a desired product, adding it to the cart, and checking out. Payment options may include credit cards or installment plans provided by the retailer.
Returns, exchanges, and warranties are also key considerations when buying lab-grown diamond rings online. Reputable online retailers often have favorable return policies in case customers are not satisfied with their purchase or wish to exchange. Warranties may also cover any potential damages or issues that may arise after purchase.
The increasing popularity of lab-grown diamond rings has been driven by the growing awareness of environmental concerns related to mining natural diamonds. With technology allowing for the creation of lab-grown diamonds that are visually identical to natural diamonds, the future looks promising. Thus, online platforms have emerged to meet the growing demand for lab-grown diamond rings and provide convenient purchase and payment options.
Returns, Exchanges, and Warranties
Lab-grown diamond rings are gaining popularity due to their sustainable and ethical sourcing. People can purchase them online with ease. Returns, exchanges, and warranties are often included with purchases. This gives customers flexibility to return or exchange their purchase if they are not satisfied. Furthermore, warranties give assurance of coverage for any potential damages or defects that may occur post-purchase.
When considering to purchase a lab-grown diamond ring online, it is best to go with reputable retailers such as James Allen, Blue Nile, Brilliant Earth, Rare Carat, or Kay Jewelers. The 4Cs – Cut Quality, Color Grade (ranging from colorless to light yellow), Clarity (ranging from flawless to included), and Carat Weight – should be taken into account when selecting a lab-grown diamond ring. Certification from accredited gemological laboratories is important for authenticity. Visual inspections and comparisons can also be conducted to assess the overall appearance and quality of the diamond.
When choosing a lab-grown diamond ring, factors such as shape, cut quality, setting style, band design, and preference for colorless or eye-clean diamonds should be considered. The purchase process usually involves selecting the desired lab-grown diamond ring, completing the payment online, providing shipping details, and confirming the order. It is advisable to review the return and exchange policies before making a purchase. Checking for any available warranties can provide further peace of mind.
Conclusion

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Randy Wright
Lab-grown diamond rings have been steadily gaining popularity in the market. In this conclusion, we will explore why these rings have become such a sought-after choice for consumers. We will also touch upon the future prospects of lab-grown diamonds, shedding light on the possibilities it holds for the jewelry industry. So, if you’re considering purchasing a lab-grown diamond ring online, read on to discover the key insights and trends that will help inform your decision.
The Growing Popularity of Lab-Grown Diamond Rings
Lab-grown diamond rings are becoming popular due to their unique features and advantages. They are created in a precise environment using advanced technology, which is the same as natural diamonds. Plus, they are more affordable, making them a great option for buyers.
Reasons for their growing popularity include:
- Sustainable and ethical alternative to natural diamonds.
- No mining or environmental harm.
- Free from conflict and unethical practices.
Customers have a wide range of choices when it comes to shape, cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Online retailers like James Allen, Blue Nile, and Kay Jewelers make it easy to access high-quality lab-grown diamonds.
When buying, buyers must check the authenticity and certification of lab-grown diamonds. Reputable retailers provide grading reports from renowned laboratories like GIA or IGI. Visual inspection and comparison can also help buyers verify the quality.
Choose the desired ring, pay through various options offered by online retailers, and check return policies and warranties provided by the seller. Also factor in shape, cut quality, setting style, band design, and colorless and eye-clean diamonds for superior appearance. Certification plays an important role in establishing the value and authenticity of the diamond.
The Future of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds, a future for jewelry, offer perks. Crafted with science, these gems share the same traits as natural diamonds – and they look just the same. Plus, they’re ethically and environmentally friendly with a lower carbon footprint since mining isn’t needed. Also, lab-grown diamonds are more precise and consistent.
Tech advancements could make production of lab-grown diamonds more economical. This could lead to lower prices and make diamond rings cheaper. Furthermore, the demand for conflict-free diamonds could drive up popularity for lab-grown diamond rings.
Research and development is also happening to expand the color range of lab-grown diamonds. At the moment, most show a near-colorless or yellowish hue. But scientists are working hard to create fancy colored lab-grown diamonds, like pinks, blues, and greens. This would give customers more choices when selecting the color for their diamond ring.
Some Facts About How To Buy a Lab Grown Diamond Ring Online:
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds are a cost-effective alternative to natural diamonds and are available in various shapes and sizes. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical composition and structure as natural diamonds, making them visually and optically identical. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds are up to 40% more affordable than mined diamonds, making them a more budget-friendly option. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds are ethical and environmentally friendly, as they are created without the humanitarian and environmental conflicts associated with the mining industry. (Source: Team Research)
- ✅ It is important to buy lab-grown diamonds from reputable vendors and review the diamond’s properties, pictures, videos, and grading report before making a purchase. (Source: Team Research)
FAQs about How Can I Buy A Lab Grown Diamond Ring Online?
How can I buy a lab-grown diamond ring online?
There are several reputable online retailers where you can buy lab-grown diamond rings, such as James Allen, Blue Nile, Clean Origin, and Brilliant Earth. These retailers offer a wide selection of high-quality lab-grown diamonds, superior ring settings, and competitive prices. Simply visit their websites, browse their collections, and choose the lab-grown diamond ring that suits your preferences.
What is the advantage of buying a lab-grown diamond ring?
Lab-grown diamond rings offer several advantages. Firstly, they are more affordable compared to natural diamond rings, often costing 10 to 50% less. Secondly, lab-grown diamonds are produced without the humanitarian and environmental conflicts associated with the mining industry, making them an ethical choice. Lastly, lab-grown diamonds are chemically and visually identical to natural diamonds, ensuring the same level of beauty and quality.
How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds in terms of quality?
Lab-grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds. They have the same hardness, strength, and durability. Lab-grown diamonds are graded and certified by leading gemological labs such as GIA, IGI, SGL, and EGL, ensuring their quality. They offer the same 4Cs (cut, color, clarity, and carat) as natural diamonds, allowing you to choose a lab-grown diamond ring with your desired specifications.
Are lab-grown diamonds as valuable as natural diamonds?
While lab-grown diamonds have the same aesthetic and gemological properties as natural diamonds, they have less resale value. Lab-grown diamonds are priced at a fraction of the cost of natural diamonds, making them more accessible to a wider range of budgets. However, it’s important to note that the value of any diamond, whether lab-grown or natural, lies in its sentimental and emotional worth rather than its resale value.
What should I look for when buying a lab-grown diamond ring online?
When buying a lab-grown diamond ring online, it is important to choose a reputable retailer that offers certification for every piece of jewelry. Look for retailers that provide clear and detailed information about the diamond’s properties, such as cut, color, clarity, and carat. It’s also helpful to check for customer reviews and compare similar diamonds to ensure you are getting the best value for your purchase.
Can I customize the lab-grown diamond ring I want to purchase?
Many online retailers that sell lab-grown diamond rings offer customization options. You can often choose the diamond shape, cut quality, ring setting, and even the metal type. Some retailers may also offer the option to request modifications to the design. If customization is important to you, it’s recommended to browse the websites of reputable retailers and see which ones provide the level of customization you desire.