How are lab grown diamonds made?
Key Takeaways:
- Lab-grown diamonds are created using two main methods: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- HPHT method involves subjecting a diamond seed to high pressure and temperature to encourage crystal growth, while CVD method involves the deposition of carbon atoms onto a diamond seed using a gaseous environment.
- Lab-grown diamonds offer several advantages over mined diamonds, including a more sustainable and ethical production process, a lower price point, and the ability to create diamonds with specific characteristics.
Background on lab-grown diamonds and their increasing popularity
Lab-grown diamonds have seen a surge in recent years. This trend is powered by various reasons. Consumers want sustainable and ethical alternatives to mined diamonds, plus technology has made it easier and faster to make lab-grown diamonds. As people become more mindful of the perks of lab-grown diamonds, their demand has risen too.
The rise of lab-grown diamonds is due to several factors. Firstly, they are a more sustainable and ethical option than mined diamonds. People care about the environment and laborers, so lab-grown diamonds are a better choice. Furthermore, technology has improved the quality of lab-grown diamonds to be indistinguishable from natural diamonds.
Lab-grown diamonds are also more affordable. They are usually cheaper than mined diamonds, making them a great option for those on a budget. Plus, you can even get custom-made designs and colors with lab-grown diamonds, which is attractive for those who want personalized jewelry.
Importance of understanding the process of making lab-grown diamonds
It is essential to understand lab-grown diamonds to get an idea of their worth and potential effect on the diamond industry. These diamonds have become popular for their ethical and sustainable qualities, as well as for looking the same as mined diamonds. Knowing how they are created helps people make informed decisions when buying jewelry and support a more eco-friendly and socially responsible industry.
Lab-grown diamonds are produced through two ways: high pressure, high temperature (HPHT) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The HPHT method replicates the natural formation of diamonds deep in the Earth’s mantle. It needs expensive equipment and monitoring of temperature and pressure. The CVD method uses ionized gases to create a plasma environment for carbon atoms to deposit and turn into a diamond crystal.
It is important for consumers, jewelers and enthusiasts to learn about the processes. The HPHT needs careful monitoring to get the diamond right. For the CVD process, exact gas composition and ionization levels are needed. Knowing these details helps people appreciate the hard work that goes into creating lab-grown diamonds and recognize their value.
In addition, lab-grown diamonds have features that set them apart from mined diamonds. They have the same hardness and sparkle, but fluorescence may vary. Mined diamonds often show fluorescence under UV light, but lab-grown diamonds usually have weak or no fluorescence. This can be used to identify diamonds that are man-made.
To sum up, understanding how lab-grown diamonds are made is vital in understanding their value and craftsmanship. Knowing the intricacies of the HPHT and CVD methods lets people appreciate the precision in making these diamonds. Recognizing unique characteristics of lab-grown diamonds also allows them to be distinguished from mined diamonds, which increases their appeal.
Overview of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Peter Adams
Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic diamonds, are revolutionizing the jewelry industry. In this overview, we’ll delve into the unique characteristics and definitions of lab-grown diamonds. Additionally, we’ll explore the advantages they offer over mined diamonds. Prepare to be amazed by the innovative techniques behind the creation of these stunning gems.
Definition and characteristics of lab-grown diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds, AKA synthetic or cultured diamonds, are made in a lab. They possess the same chemical and physical properties as natural diamonds. They’re produced using the HPHT or CVD method. Lab-grown diamonds have the same crystalline structure, hardness, brilliance, and fire as mined diamonds.
Technology replicates the conditions found deep within Earth’s mantle. HPHT involves subjecting a seed diamond to high pressure and high temperature with a carbon-rich source. This causes carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed diamond. CVD involves exposing a substrate to a carbon-rich gas at low pressure and high temperature. This leads to the growth of diamond layers on top of the substrate.
Lab-grown diamonds are unique. They can be made with high levels of clarity and color consistency. They can be customized to meet specific requirements, making them desirable for jewelry and industrial apps.
Lab-grown diamonds are eco-friendly. They require less energy and water compared to mining. And, they’re conflict-free, not contributing to unethical practices associated with some diamond mining. (Reference: Diamond Foundry)
Advantages of lab-grown diamonds over mined diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds have lots of benefits over mined diamonds. They share the same physical and chemical qualities, meaning they are indistinguishable. Here are the three main advantages:
- They are more eco-friendly since they use less energy and water in production.
- They offer conflict-free assurance as opposed to mined diamonds.
- They are more affordable due to their recent advances in technology.
Plus, they come in larger sizes, specific colors, and boast precise control over their characteristics. This has led to improved production techniques and quality standards.
Before choosing between lab-grown and mined diamonds, consider personal preferences and values. Mined diamonds may have a sentimental or historic significance that can’t be replicated.
High Pressure, High Temperature Method
Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Christopher Roberts
The High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) method is a fascinating process used to create lab-grown diamonds. In this section, we will explore the ins and outs of this method and unravel its purpose. Additionally, we’ll take a step-by-step journey through the process of growing lab-grown diamonds using the HPHT method. Get ready to uncover the science behind the creation of these stunning diamonds.
Explanation of the HPHT method and its purpose
Interest and demand for lab-grown diamonds is growing rapidly. The HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) method is a popular way to create them. This method involves intense pressure and temperature, similar to what is found deep in the Earth’s core.
A seed diamond is placed in a growth cell with carbon from graphite. The cell is then exposed to heat of 1,500 Celsius and pressure up to 5 GPa. The carbon atoms dissolve into metal catalysts and move towards the seed diamond.
The carbon atoms start to crystallize and form new diamond layers on the seed diamond. Over time, the diamond grows. The process can take a few weeks to several months.
The HPHT method is special because it replicates the high pressure and temperature found in the Earth, producing diamonds with similar chemical compounds and crystal structures.
The HPHT method offers benefits. Firstly, it allows diamonds to be grown with specific characteristics. Secondly, it is ethical and reduces environmental impact. Finally, it increases affordability and accessibility of diamonds.
Step-by-step process of growing lab-grown diamonds using HPHT
Lab-grown diamonds are crafted using the HPHT method. This involves high pressure and temperature in a chamber to grow a larger diamond from a diamond seed. The steps to this process are:
- Selecting a diamond seed.
- Preparing a HPHT chamber.
- Applying high pressure.
- Adding high temperature.
- Cooling and cleaning.
These conditions help form a diamond with similar characteristics and quality to mined diamonds. As research and technology progresses, this production method can be expected to improve and become more popular.
Chemical Vapor Deposition Method

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Ralph Ramirez
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a fascinating technique used in the creation of lab-grown diamonds. In this section, we will delve into the purpose of the CVD method and walk through the step-by-step process of growing diamonds using this innovative approach. With a mix of precise chemical reactions and controlled conditions, the CVD method allows us to produce high-quality diamonds that possess the same characteristics as their natural counterparts. Let’s uncover the science behind this captivating process.
Explanation of the CVD method and its purpose
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a way of growing lab-grown diamonds. It uses a process that places carbon atoms onto a base to form diamond crystals. The goal is to make diamonds with chemical and physical properties that are similar to mined diamonds.
The CVD method uses a gas like methane and hydrogen, heated to 800-1200 degrees Celsius. The gases are put onto a base made of diamond or other materials. The carbon atoms connect to the base and form layers of diamond crystals.
This method can be used to control the growth of the diamond at the atomic level. This helps to adjust the diamond’s color and clarity. It can also create larger, more uniform diamonds than other methods.
The CVD method is efficient and produces high-quality lab-grown diamonds. As technology progresses, it is predicted to play an important role in making sustainable, ethical diamonds without sacrificing quality or beauty.
Step-by-step process of growing lab-grown diamonds using CVD
Lab-grown diamonds can be made by Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). A gas with carbon is heated in a vacuum chamber to 800-1000°C. This breaks down the carbon molecules, releasing atoms or clusters. These settle on a diamond seed or plate, forming a diamond layer. This continues until the desired size and quality of diamond is formed.
First, the diamond seed or plate is cleaned and polished. It then goes into the vacuum chamber with the gas mixture. The chamber is sealed, and air and contaminants are removed. It is heated to high temperatures for hours or days.
The carbon atoms form a thin layer of diamond, which bonds with the previous layers, to create a solid crystal. This allows for precise control. The diamond is then removed and cut and polished.
CVD is a precise and controlled way to make diamonds like mined ones. It also allows for customizing properties, and is more sustainable than mining.
Comparison between HPHT and CVD Methods

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Joe Wilson
When it comes to creating lab-grown diamonds, the HPHT and CVD methods are at the forefront. In this section, we’ll compare these two methods, highlighting their similarities and differences. Additionally, we’ll explore the benefits and drawbacks of each method, as well as the key factors to consider when choosing between HPHT and CVD-grown diamonds. So, if you’re curious about the techniques behind lab-grown diamonds, stay tuned for an insightful comparison.
Similarities and differences between the two methods
Lab-grown diamonds are created with two methods: HPHT and CVD. Here’s a table that shows the similarities and differences between them:
| HPHT Method | CVD Method |
| High pressure and high temperature. | Carbon deposited from vapor. |
| Diamond seed in pressurized chamber. | Gases heated to extreme temperatures. |
| Heat and pressure applied for hours. | Carbon atoms bond onto substrate. |
The HPHT method has been around for longer than CVD. HPHT first came out in the mid-20th century, while CVD popped up in the late 20th century.
Also, both methods produce lab-grown diamonds with similar optical properties to mined diamonds. They have the same sparkle, fire, and brilliance.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method
Lab-grown diamonds can be made with two methods: HPHT and CVD. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
For HPHT, the pros include creating large, high-quality diamonds, and they are cheaper than mined diamonds. They also come in desirable colors and clarity. But, it requires big, costly machines and procedures. It also can’t make many diamonds at once. And some say HPHT-made diamonds lack rarity.
CVD-made diamonds have controlled growth parameters, and can make lots of diamonds. But, they cost more and take longer to grow. Yet, their hardness is superior to natural ones.
When picking between these two kinds of diamonds, think about cost-efficiency, scalability, and rarity. It’s like deciding between a spicy taco or a cheesy pizza – both delicious!
Factors to consider when choosing between HPHT and CVD-grown diamonds
A table can help buyers decide between HPHT and CVD-grown diamonds. It should include factors like Method, Cost, Time Required, Quality Control, Environmental Impact, and Availability. Comparing the factors side-by-side enables buyers to make the right decision based on their priorities.
One may consider jewelry requirements or personal values when choosing between HPHT and CVD-grown diamonds. Taking these unique details into account helps buyers make sure their purchase meets their desires and needs.
Lab-grown diamonds are an ethical alternative to mined diamonds. A GIA study reveals that over 70% of participants cannot tell the difference without specialized equipment. This similarity in appearance makes lab-grown diamonds popular in the market.
Identifying Lab-Grown Diamonds
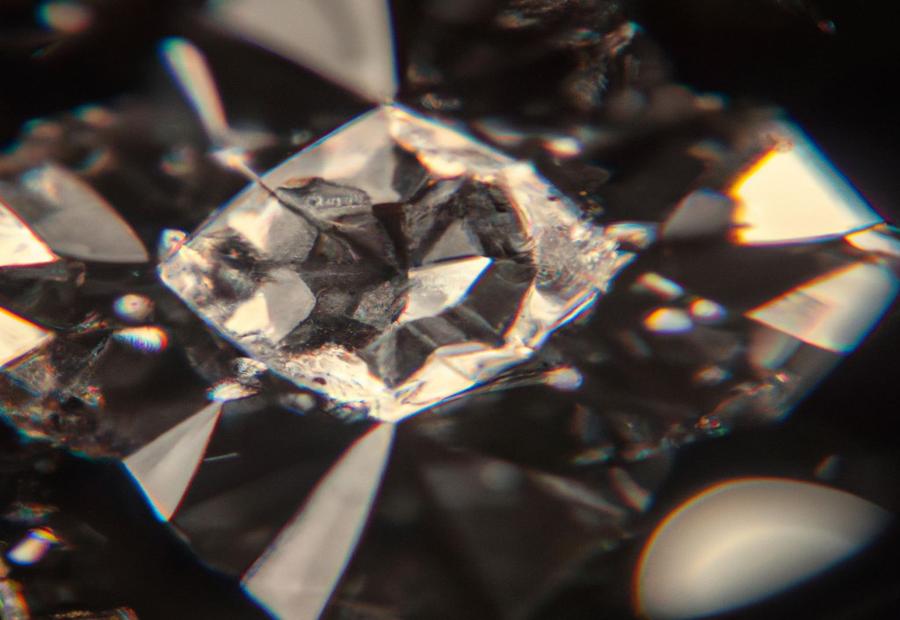

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Christopher Nguyen
Lab-grown diamonds have become a popular choice for those seeking an ethical and sustainable alternative to mined diamonds. In this section, we will explore the various ways of identifying lab-grown diamonds. From grading reports that indicate if a diamond is HPHT or CVD-grown, to specific characteristics that set them apart from mined diamonds, we will provide you with the tools to distinguish between these two types. Join us as we dive into the fascinating world of lab-grown diamonds and unveil their unique features.
Grading reports and indications of HPHT or CVD-grown diamonds
To comprehend grading reports, it’s helpful to make a table. This table should categorize particular characteristics of HPHT and CVD-grown diamonds. One column could include indicators like metallic inclusions or growth patterns typical of HPHT-grown diamonds. The other column could list indicators like flat plate-shaped nitrogen defects or orange fluorescence that usually occur with CVD-grown diamonds. This visual representation helps jewelers and consumers quickly recognize the production technique used for a diamond based on its special features.
Apart from the indicators specified in grading reports, there are other markers that can help identify HPHT or CVD-grown diamonds. For instance, when magnified, certain differences in appearance compared to mined diamonds can be seen. These differences may involve distinct growth lines or color zoning patterns not usually found in natural diamonds. By being aware of these unique details and using them together with grading reports, people can make wise decisions when buying lab-grown diamonds.
An illustration of how significant grading reports and indications are when knowing what type of diamond you own is this: someone bought what was supposed to be a mined diamond from an online seller with no documentation. But, after a reputable gemologist inspected it with specialized equipment and referred to relevant grading reports for comparison, they concluded the diamond was CVD-grown. This story underlines the importance of grading reports and indications in recognizing the origin and production method of diamonds, ensuring transparency within the jewelry industry.
Lab-grown diamonds: science meets style, without having to worry about supporting unethical mining practices.
Characteristics to look for in lab-grown diamonds
Gemologists and customers can identify distinct features of lab-grown diamonds. These traits indicate the source and verify the authenticity of the diamond.
- One thing to consider is the even quality. Unlike mined diamonds, which can vary in color and clarity, lab-grown diamonds are usually consistent.
- Also, lab-grown diamonds are usually free of certain faults that are found in mined diamonds, which makes them more attractive and potentially higher clarity.
- Moreover, lab-grown diamonds may have growth lines, which come from the manufacturing process. These lines do not harm the diamond but make it unique.
It is essential to check documentation from reliable gemological labs while examining lab-grown diamonds. This ensures customers make the right decision, knowing all of the specific features of lab-grown diamonds.
Do not miss out on the chance to own lab-grown diamonds, due to their exclusive qualities and the growing trend that follows. Knowing these characteristics will give consumers the confidence to get a stunning piece of jewelry that reflects their values.
Differences in appearance compared to mined diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds have visible differences when compared to mined ones. These distinctions come from the various methods used in their creation.
- Lab-grown diamonds may be more consistent in color, whereas mined diamonds can be of a wider range due to impurities or structural defects.
- Lab-grown diamonds can have fewer inclusions since they’re grown in controlled conditions, while natural diamonds can have more inclusions due to their formation process.
- Their clarity can be higher in lab-grown diamonds, due to being produced in controlled environments.
- Lab-grown diamonds can have distinct growth patterns which can give them unique visuals.
- The fluorescence of lab-grown diamonds can vary from those of mined ones.
- The overall brilliance and fire of the two types may differ, due to differences in their crystal structure and composition.
These variations in looks don’t decrease their beauty or worth, instead, they make lab-grown diamonds special and let experts differentiate them from mined diamonds by seeing them. Lab-grown diamonds offer a perfect alternative for people looking for diamonds with unique appearances, that reflect their modern origin. Get ready to see a bright, shiny, scientifically amazing future with these gems!
Conclusion

Photo Credits: Www.Lab-Grown-Diamond-Ring.Com by Joshua Perez
In conclusion, let’s recap the benefits and process of making lab-grown diamonds and explore their future impact on the diamond industry. We’ll reflect on the advantages they offer in terms of ethical sourcing and environmental sustainability, as well as their comparable quality to natural diamonds. Additionally, we’ll touch upon the potential changes they might bring to the traditional diamond market and discuss the ongoing debate surrounding their acceptance and recognition within the industry.
Recap of the benefits and process of making lab-grown diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds offer many advantages and the process of making them involves special techniques. These synthetic diamonds are formed using two main methods: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- HPHT Method: A tiny diamond seed is placed in a growth chamber with carbon-rich gases. Then, high pressure and temperatures up to 2000 degrees Celsius are applied. This causes the carbon atoms to crystallize and stick to the diamond seed, resulting in a bigger lab-grown diamond.
- CVD Method: A thin slice of diamond called a substrate is placed in a vacuum chamber. Carbon-rich gases break down into individual carbon atoms, which settle onto the substrate and layer up over time. This is done multiple times until the size and quality of the lab-grown diamond is achieved.
- Advantages of Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds are popular for various reasons. First, they have the same physical and chemical properties as mined diamonds, but don’t have ethical or environmental issues associated with mining. Second, they cost less than natural diamonds, making them more accessible. Lastly, they are free from conflicts linked to diamond trading.
Lab-grown diamonds have distinct features that set them apart from mined diamonds. Grading reports can reveal if a diamond was grown using HPHT or CVD methods. Furthermore, certain features such as internal color zoning or strange crystal shapes might signify the diamond is lab-grown rather than naturally formed.
Closing remarks on the future of lab-grown diamonds and their impact on the diamond industry
The future of lab-grown diamonds looks bright. Their impact on the diamond industry is expected to be huge. Lab-grown gems are a sustainable and ethical alternative to mined diamonds, tackling environmental damage and human rights issues. With technology, their quality and affordability are improving. This rising popularity could disrupt the diamond industry. Traditional mines may struggle with a decline in demand for mined diamonds.
Lab-grown diamonds offer advantages. They have consistent color, clarity, and carat weight. Also they provide flexibility in terms of size and shape. Plus, production methods, such as HPHT and CVD, are becoming more efficient and cost-effective. This could help drive down prices, making them accessible to more people.
In conclusion, lab-grown diamonds are transforming the diamond industry. Their sustainable and ethical nature, plus advantages in price and quality control, make them a great alternative to mined diamonds. As technology progresses, we can expect lab-grown diamonds to become more popular and reshape the entire diamond market.
Some Facts About How are lab-grown diamonds made?
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds are more sustainable, affordable, and ethically sourced compared to mined diamonds. (Source: Ritani)
- ✅ Lab-grown diamonds are optically, physically, and chemically identical to mined diamonds and can be tested as such. (Source: Ritani)
- ✅ There are two methods for growing lab diamonds: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). (Source: Ritani)
- ✅ HPHT diamonds are grown using extreme heat and pressure to replicate the conditions that form diamonds underground. (Source: Ritani)
- ✅ CVD diamonds are grown in a vacuum chamber with carbon-rich gases and have a chemically pure composition. (Source: Ritani)
FAQs about How Are Lab Grown Diamonds Made?
How are lab grown diamonds made?
Lab grown diamonds are made using two processes: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In the HPHT method, a small diamond seed is placed in carbon and subjected to extreme heat and pressure to replicate the conditions that form diamonds underground. In the CVD method, a diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber with carbon-rich gases and heated. Both methods result in visually indistinguishable diamonds that are chemically, physically, and optically identical to mined diamonds.
What is the HPHT method for growing lab diamonds?
The HPHT method is the original process used to grow lab diamonds. It involves placing a small diamond seed in carbon and subjecting it to extreme heat and pressure. This method replicates the conditions that form diamonds underground and can also be used to enhance diamond color. HPHT diamonds tend to have a yellowish hue and darker metallic inclusions, which can make them magnetic. Grading reports can specify if a diamond is HPHT-grown, and some HPHT diamonds may have a blue tint.
What is the CVD method for growing lab diamonds?
The CVD method is a newer process for growing lab diamonds. It imitates diamond formation in interstellar gas clouds and uses less pressure and smaller machines compared to the HPHT method. In the CVD method, a diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases and heated. CVD diamonds are Type IIA diamonds, which are chemically pure and lack nitrogen and boron impurities. They do not have metallic inclusions and are not magnetic. Grading reports can indicate if a diamond is CVD-grown, and CVD diamonds may have strain lines and fluoresce under UV light.
How do lab grown diamonds compare to mined diamonds?
Lab grown diamonds are optically, physically, and chemically identical to mined diamonds. They have the same carbon structure and can be tested as diamonds with a diamond tester. Lab grown diamonds are a sustainable and ethical alternative to mined diamonds, as they are more affordable and ethically sourced. The growth processes used to create lab grown diamonds result in visually indistinguishable diamonds that share the same characteristics as nature’s finest.
Can lab grown diamonds be identified?
Lab grown diamonds can be identified through grading reports. These reports can specify if a diamond is HPHT-grown or CVD-grown. HPHT diamonds may have a yellowish hue, darker metallic inclusions, and a magnetic response. CVD diamonds, on the other hand, may have strain lines and fluoresce under UV light. However, visually, both lab grown diamonds and mined diamonds are indistinguishable.
What is the process of grading lab grown diamonds?
Lab grown diamonds go through a similar grading process as mined diamonds. They can be graded for cut, color, carat, and clarity. Grading reports for lab grown diamonds also specify whether they are HPHT-grown or CVD-grown. These reports provide information about the origin and growth method of the diamond, allowing consumers to make informed choices.



Leave a Reply